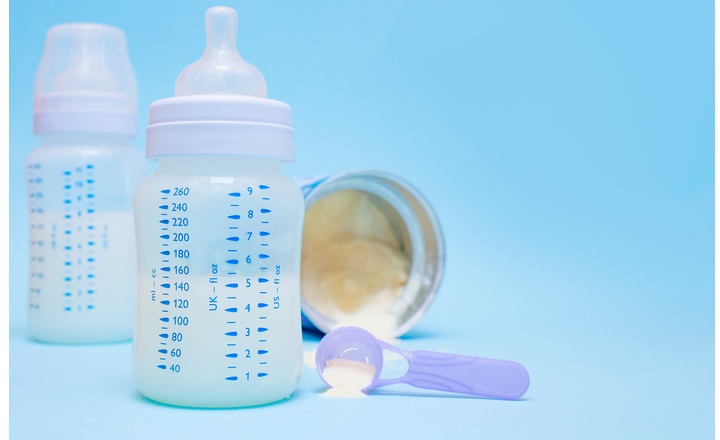
- PIF is not sterile and must therefore be reconstituted and handled carefully to minimize infection risk for infants.
- Infants - particularly newborns - have underdeveloped immune systems and immature gut barriers, making them especially vulnerable to infections from foodborne microbes. Contaminated formula poses risks to gut health and potential infection.
- Current guidelines recommending reconstitution with ~70°C water may not reliably inactivate all contaminants.
Key Findings: Cairns et al. obtained 21 PIFs representing 5 different UK commercial brands.1 The PIF samples were prepared using 1) sterile 70°C water, 2) sterile room temperature water, or 3) a popular at-home preparation machine (AHPM). Following routine culture (TSA for bacteria and SAB for yeast), isolates were identified via MALDI-ToF.
- Recoverable microorganisms were detected across brands and product types, regardless of preparation method.
- Bacillus, Candida, and Cupriavidus spp. Accounted for 84.6% of all recovered isolates.
- Bacillus cereus isolates survived reconstitution at 70°C, demonstrating heat resistance consistent with prior literature.
- Microbial profiles did not differ significantly between brands or product types; however, preparation method significantly influenced microbial recovery (P < 0.05):
- Sterile room-temperature and sterile 70°C water yielded similar, low-level recoveries.
- AHPM-based preparation showed the highest diversity and abundance of contaminants, including Candida guilliermondii, Cupriavidus pauculus, Moraxella spp., and Virgibacillus proomi, all of which were solely isolated from the AHPM-prepared samples.
- Contaminants associated with the AHPM were linked to the manufacturer-supplied water filter, suggesting the device itself is a potential source of contamination.
The study concludes that current recommended reconstitution practices may not reliably eliminate all microbial contaminants present in PIF, and that the issue may reflect minor environmental contamination occurring at the production or packaging stage or, in some instances, within the preparation setting.
Bigger Picture:
This study raises important concerns about microbial safety in powdered infant formula, a product universally used for a highly vulnerable population. The presence of viable organisms - even after recommended preparation - suggests a need to revisit hygiene controls, manufacturing standards, and consumer guidance. It also highlights broader gaps in safety validation for low-moisture foods that are later reconstituted, emphasizing the importance of microbial monitoring and process reassessment for products consumed by high-risk groups.
(Image Credit: iStock/Olena Zalevska)