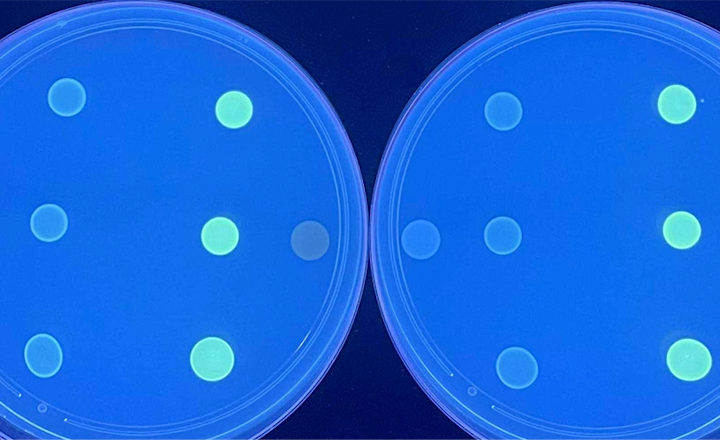
BD Diagnostics has received FDA clearance to market the BD MAX™ MRSA XT Assay for use on the fully-automated BD MAX™ System. This is the second assay from BD Diagnostics capable of detecting newly emerging MRSA strains with the novel mecC gene. Launched in 2013, the BD MAX™ StaphSR Assay reports results for both Staphylococus aureus (SA) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococus aureus (MRSA) and was the first commercially available assay in the U.S. to detect mecC strains of MRSA. Both assays use eXTended Detection Technology to identify a broad range of SA strains including mecA and mecC dropout mutants and new strains of MRSA that may not be detected by other assays.
Molecular assays for MRSA are used in active surveillance programs to identify colonized patients rapidly. Active surveillance is a proven strategy to reduce transmission in healthcare settings and helps prevent infection in vulnerable patients.[i] Inaccurate detection may contribute to uncontrolled transmission of MRSA and inappropriate use of healthcare resources. With many commercial assays, SA strains carrying SCCmec where the mecA gene is absent (commonly called “dropout mutants”) may be incorrectly classified as MRSA. These false positive results can lead to unnecessary and expensive isolation and treatment of patients.[ii] MRSA strains with the newly emerging mecC gene account for nearly three percent of all new MRSA cases[iii] in some communities but cannot be detected by all assays.[iv] These false negative results can lead to uncontrolled transmission of undetected strains of MRSA.[v]
The BD MAX MRSA XT Assay is the latest milestone demonstrating BD’s commitment to providing advanced assays to detect and prevent HAIs. Other HAI assays available on the BD MAX System include BD MAX™ Cdiff for the detection of toxigenic Clostridium difficile DNA, and BD MAX StaphSR. BD MAX™ HAI Solutions combine efficiency through system automation with the flexibility to perform multiple HAI assays in the same run, allowing hospital laboratories to customize testing in response to current and future challenges in the fight against HAIs.
References: [i] Jain et al., N Engl J Med 2011;364:1419-30. Veterans Affairs Initiative to Prevent Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infections
[ii] Blanc et al., JCM 2011;49:722-724. High Proportion of Wrongly Identified Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Carriers by Use of a Rapid Commercial PCR Assay Due to Presence of Staphylococcal Cassette Chromosome Element Lacking the mecA Gene.
[iii] Petersen et al., Epidemiology of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus carrying the novel mecC gene in Denmark corroborates a zoonotic reservoir with transmission to humans Clin Micro Infect 2013;19:E16-E22
[iv] Shore et al., Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 2011;55:3765-3773
[v] Worby et al., Am J Epidemiology advanced access published online April 16, 2013. Estimating the Effectiveness of Isolation and Decolonization Measures in Reducing Transmission of Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Hospital General Wards