Spoilage microorganisms can cause increased turbidity, color changes and unpleasant sensory properties in juices. The growing demand for natural organic drinks has made microbiology quality control of juice production processes even more crucial. Acidophilic bacteria like Alicyclobacillus, with their characteristic slow and late growth, pose a challenge for juice manufacturers. These microbes do not grow in juice concentrates but remain viable for a long time—their spores can germinate in the diluted (finished) product. Alicyclobacillus spores can also survive a typical pasteurization process. Detection of these organisms, which is traditionally done by incubation on a culture medium, takes five to twelve days or even longer.
The spoilage organism Alicyclobacillus can be detected and identified by HybriScan® I Alicyclobacillus spp. in about half the overall time (including enrichment) that IFU Method No. 12 takes, and with the accuracy of a genetic test but without the need for PCR. The rapid, low-cost molecular test system with live/dead cell differentiation is very robust, with no inhibitory effects from the sample matrix. After a 72-hour enrichment with YSG or our IFU 12 conform BAT Broth the test can be performed in 2 hours, after which a color change indicates a positive result. It is also possible to identify colonies on K, YSG or our IFU 12 compliant BAT Agar (see Figure 1) by picking some test material. The detection/confirmation step is what vastly speeds up testing: it takes only 2 hours with HybriScan® Alicyclobacillus spp. but 72 hours (3 days) according to IFU Method No. 12.
No expensive equipment is needed, just the simple test in a microplate format. All known Alicyclobacillus beverage spoilage species are detected in a single test.
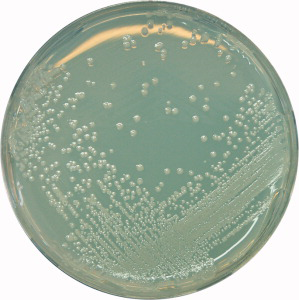
Figure 1: Alicyclobacillus acidoterrestris DSM 2498 on BAT agar
Principle:
The HybriScan® method is based on the detection of rRNA via hybridization events and specific capture and detection probes. Sandwich hybridization is very sensitive, detecting attomoles of the respective target rRNA molecules providing sensitivity in crude biological samples because it is not susceptible to matrix interference. A capture probe is used to immobilize the target sequence on a solid support plate. A digoxigenin-labeled detection probe provides an enzyme-linked optical signal read-out. Detection of the desired targets results from application of anti-DIG-horseradish peroxidase Fab fragments. The bound complex is visualized by adding horseradish peroxidase substrate (TMB) to finally result in a yellow color that can also be measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader. More details about the technology and an overview of the test can be found on SigmaAldrich.com/HybriScan.
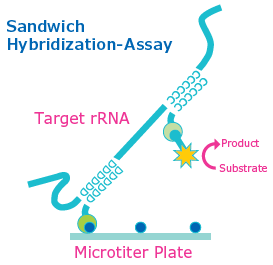
Figure 2: rRNA based detection with the HybriScan® system
Watch a video on the advantages of HybriScan® technology over other microbial detection techniques here or click on the 'Request Information' button below