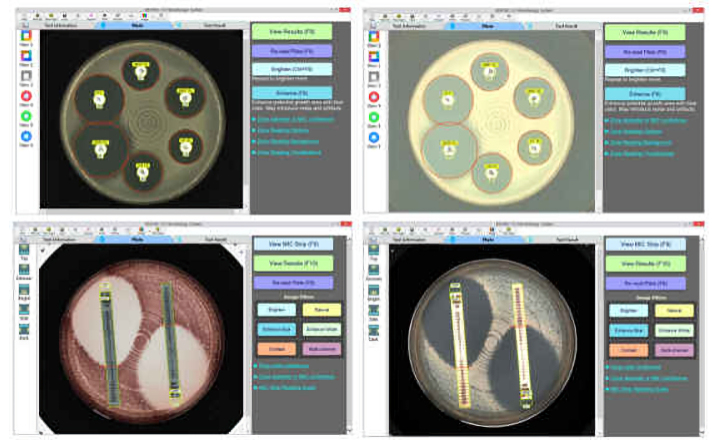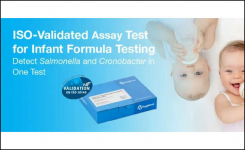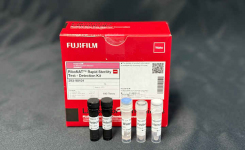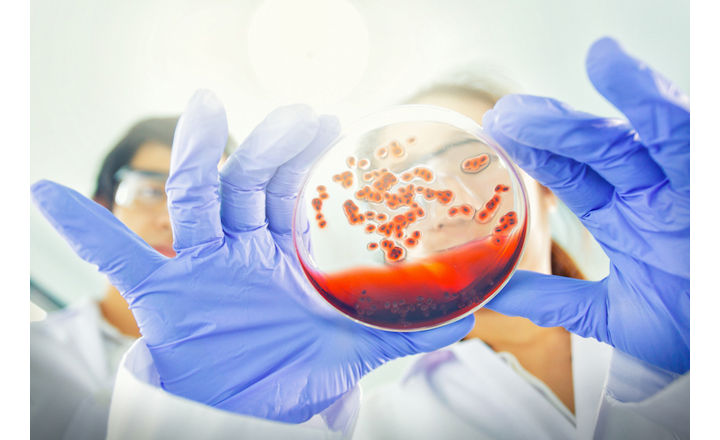
The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST) develops, validates, and provides AST methods.
Throughout the year, the EUCAST Development Laboratories (EDLs) network works to harmonize clinical breakpoints for existing antimicrobial agents (AMA) across Europe, determine breakpoints for new AMAs, and revise ones as required.
Every year, the network of EDLs submit posters to ECCMID for display at the annual conference. Each poster is a study performed by an EDL, such as: evaluating AST media on the market; reducing incubation times in a particular method; or providing data for MIC breakpoints on new AMAs.
At ECCMID 2022, EUCAST took a new approach. Professor Laurent Dortet, an ECCMID Young Researcher awardee in 2019, gave a virtual walkthrough of the different EDL posters submitted to ECCMID on Standardized Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing elucidating the reasoning behind each study, and the significance of the results and their conclusions.
In this review, we only selected studies that specifically evaluated commercial brands:
The quality of 10 brands of pre-poured commercial Mueller-Hinton plates for disk diffusion – a EUCAST evaluation (Ahman et al., 2022)
In 2020, a warning against using certain Mueller Hinton (MH) dehydrated media brands for in-house agar was published on EUCAST’s website. The warning came from a EUCAST evaluation of 21 commercially available brands that discovered only six brands of MH agar (Bio-Rad, Biolife, Oxoid, Sigma MH 2, BD BBL MH II, and CRITERION) demonstrated excellent performance. The rest had problems with one or more classes of AMAs.
In 2021, Jenny Ahman and her EDL team in Växjö, Sweden, evaluated pre-poured MH agar and compared these with the aforementioned evaluated in-house (dehydrated) media.
The best ratings observed for pre-poured MH agar were from BD, bioMérieux, and Hardy Diagnostics, with >97% of results within QC ranges. For most brands, the performance of pre-poured agar plates was poorer compared to in-house produced plates.
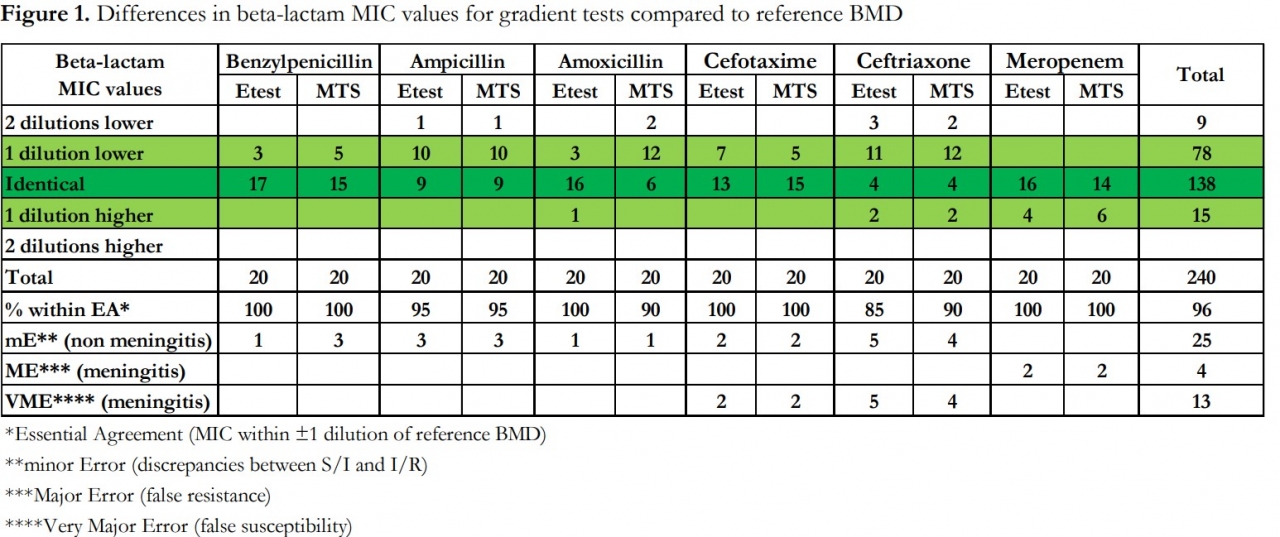
Evaluation of gradient tests for MIC determination of six beta-lactam antibiotics in Streptococcus pneumoniae using a CCUG/EUCAST collection of S. pneumoniae with defined susceptibility (Agnes Holmgren et al., 2022).
The EUCAST oxacillin 1 ug disk screening test detects all beta-lactam resistance mechanisms in Streptococcus pneumoniae, but for screen-positive isolates (oxacillin less than 20mm or less than 9mm depending on agent), MIC determination is needed.
Gradient tests are often first choice for MIC testing in clinical laboratories. EUCAST has previously shown that benzylpenicillin gradient tests underestimate MICs in S. pneumoniae.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the performance of gradient tests (Etest® from bioMerieux™ and MIC Test Strip (MTS)® from Liofilchem™) for six clinically relevant beta-lactam agents for S. pneumoniae using a CCUG/EUCAST collection of strains with defined susceptibility and compare with broth microdilution (BMD) results. Quality control was performed with S. pneumoniae ATCC 49619.
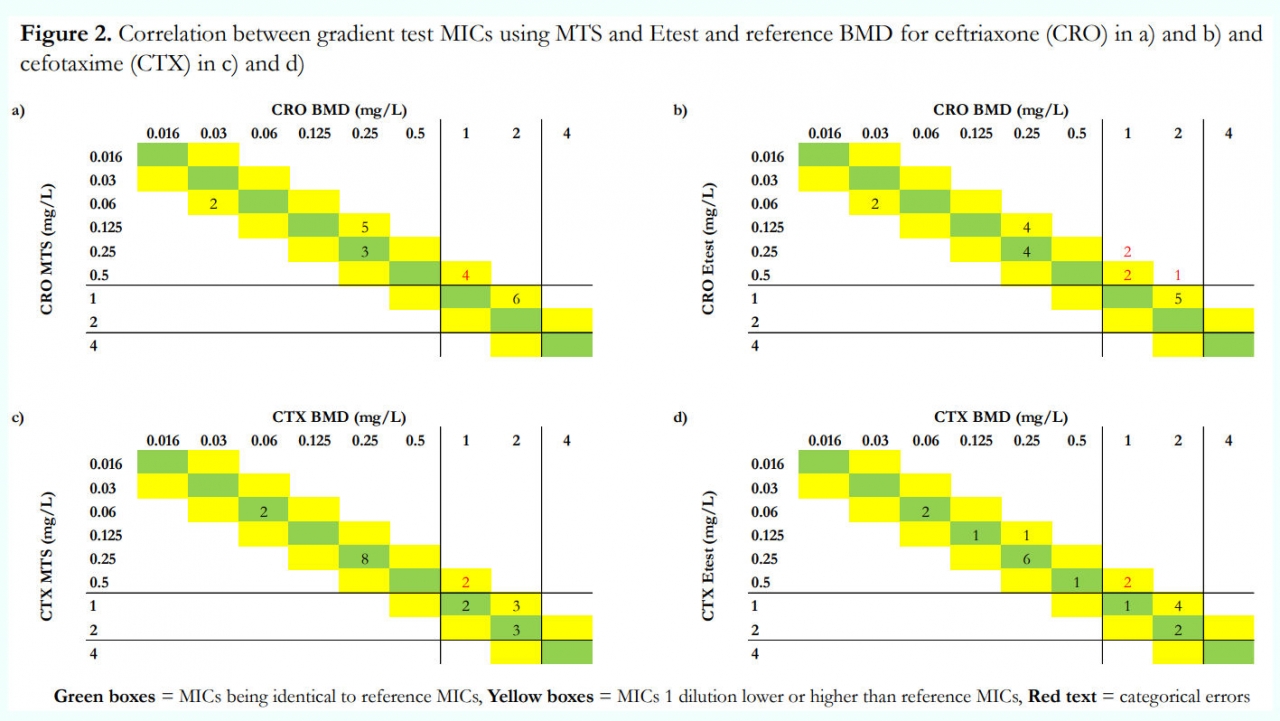
Result: There was a tendency towards lower MICs with gradient tests compared to BMD, even though most values were within EA (Figure 1). This was most pronounced for ampicillin, amoxicillin, and ceftriaxone (Figure 2). For benzylpenicillin, cefotaxime, and meropenem, gradient tests correlated better with BMD, but errors occurred. Ampicillin was the only antibiotic for which S. pneumoniae ATCC 49619 could detect these discrepancies.
 Figures and tables presented at ECCMID 2022 and used with permission and copyrighted to: Agnes Holmgren, Frida Nilsson (Clinical microbiology, Blekingesjukhuset, Karlskrona, Sweden) and Erika Matuschek (EUCAST development laboratory, Växjö, Sweden)
Figures and tables presented at ECCMID 2022 and used with permission and copyrighted to: Agnes Holmgren, Frida Nilsson (Clinical microbiology, Blekingesjukhuset, Karlskrona, Sweden) and Erika Matuschek (EUCAST development laboratory, Växjö, Sweden)
Conclusion:
Gradient tests from two manufacturers underestimated MIC values for beta-lactam agents in S. pneumoniae, mainly for isolates with higher MICs.
Results close to the breakpoints, therefore, need to be taken into careful consideration by performing supplemental BMD or introducing a local area of uncertainty. S. pneumoniae ATCC 49619 might be unable to detect these deviations. This study shows that the CCUG/EUCAST collection is an essential complement for validating MIC methods for beta-lactam agents in S. pneumoniae in clinical laboratories.
Comparison of Lefamulin MIC Test Strip (MTS) to Broth Microdilution MIC for Streptococcus spp., S. aureus, M. catarrhalis, and Haemophilus spp. (L. Koeth et al., 2022)
Lefamulin is a novel oral and intravenous (IV) pleuromutilin approved in Europe and the U.S. for community-acquired bacterial pneumonia (CAP) in adults with S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, and H. influenzae.
Lefamulin MIC Test Strip (MTS; Liofilchem) is a gradient susceptibility testing method that is FDA cleared and CE marketed. This study compared MTS to reference broth microdilution (BMD) for lefamulin susceptibility testing.
Overall, there was a good correlation of MIC results generated with MTS and BMD for lefamulin against the common CAP pathogens S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, and H. influenzae (>97% EA and CA).